Building Materials Overview in Civil Engineering
Building Materials form the foundation of civil engineering construction. Selection depends on factors like strength, durability, cost, availability, sustainability, aesthetics, and environmental conditions. Materials must comply with standards (e.g., IS codes in India, ASTM internationally) for quality and safety.
Classification of Building Materials
- Natural Materials: Stone, timber, clay.
- Manufactured Materials: Bricks, cement, concrete, steel.
- Composite Materials: Reinforced concrete, plywood.
- Modern/Sustainable: Glass, aluminum composites, recycled materials.
Here are common building materials illustrated:
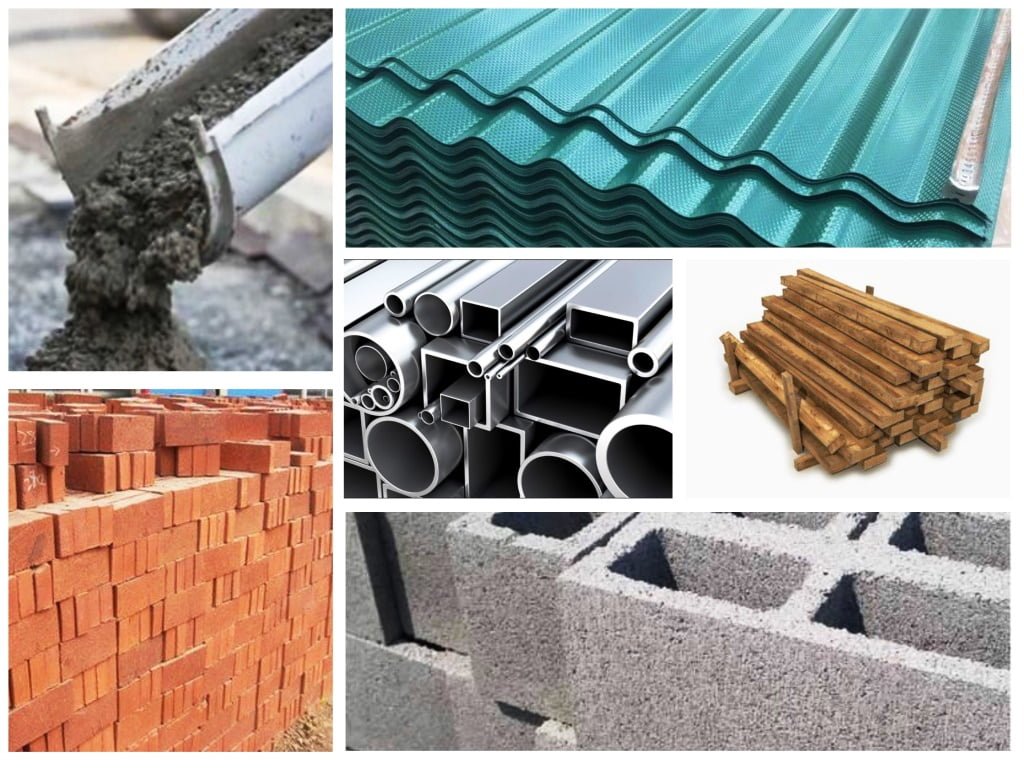


1. Bricks
- Made from clay, molded, dried, and burnt in kilns.
- Properties: Compressive strength (3.5–35 MPa), durable, fire-resistant, good insulation.
- Types: Common burnt clay bricks, fly ash bricks (eco-friendly), concrete bricks, engineering bricks.
- Uses: Walls, partitions, pavements.
2. Cement
- Binding material; main types: Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC), Rapid Hardening, etc.
- Manufacturing: Crushing limestone + clay → raw meal → kiln (clinker) → grinding with gypsum.
![Typical cement manufacturing process flow diagram [4]. | Download ...](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262607988/figure/fig1/AS:733766125371393@1551954885368/Typical-cement-manufacturing-process-flow-diagram-4.jpg)

- Properties: Sets with water, gains strength over time (28-day compressive strength ~33–53 MPa for OPC).
- Uses: Mortar, concrete, plaster.
3. Concrete
- Composite: Cement + fine aggregate (sand) + coarse aggregate (gravel) + water.
- Reinforced Concrete (RCC): Steel bars added for tensile strength.


- Properties: High compression, low tension (hence reinforcement), durable, versatile.
- Types: Plain, reinforced, prestressed, lightweight.
- Uses: Foundations, beams, slabs, columns.
4. Steel
- Alloy of iron + carbon; high tensile strength.
- Forms: Mild steel (Fe415/Fe500 TMT bars), high-yield strength deformed (HYSD) bars.
- Properties: Ductile, strong in tension/compression, corrosion-resistant with coatings.
- Uses: Reinforcement in RCC, structural frames, bridges.
5. Timber/Wood
- Natural, renewable; softwood (pine) vs hardwood (teak, oak).
- Properties: Good insulation, lightweight, aesthetic, but prone to decay/insects (treat with preservatives).
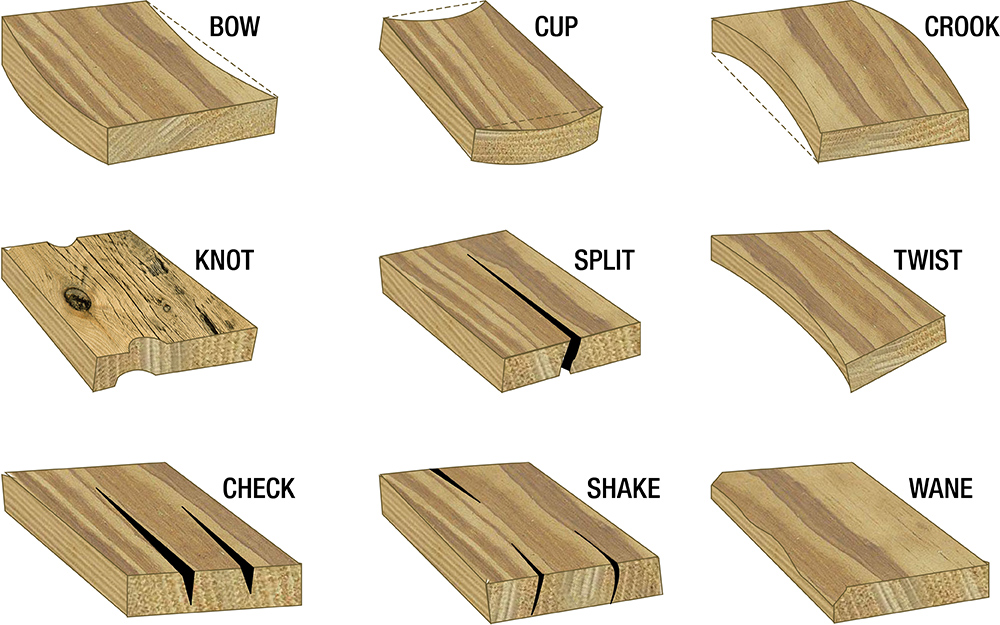

- Uses: Doors, windows, roofing, formwork, furniture.
6. Other Important Materials
- Aggregates: Sand, gravel – fillers in concrete.
- Stone: Granite, marble – flooring, cladding.
- Glass: Windows, facades.
- Modern Composites: Aluminum composite panels (ACP), fiber-reinforced plastics – lightweight, sustainable.



- Sustainable Options: Fly ash bricks, recycled concrete, bamboo.
In civil engineering, material testing (e.g., compressive/tensile tests) ensures quality. Sustainability is increasingly important – reducing carbon footprint via green materials.
Tags:
Building Materials
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bricks-types-uses-and-advantages-844819-v4-dfd8be11b5034809aa3d9a2f117ad79b.png)
