Cement in Civil Engineering
Cement is the primary binding material in modern construction, acting as a glue that holds aggregates together in concrete and mortar. The most common type is Portland Cement, invented in 1824, known for its hydraulic properties—it sets and hardens by reacting with water (hydration), even underwater.
Chemical Composition of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
Typical compounds (Bogue's compounds):

- Tricalcium Silicate (C₃S): 40–60% (early strength).
- Dicalcium Silicate (C₂S): 15–30% (long-term strength).
- Tricalcium Aluminate (C₃A): 5–12% (quick setting, heat evolution).
- Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite (C₄AF): 5–10% (color, minor strength).
Manufacturing Process
Main steps (Dry Process is most common):
- Raw material extraction (limestone, clay).
- Crushing and proportioning.
- Grinding to raw meal.
- Heating in kiln (1450°C) → Clinker formation.
- Cooling and grinding clinker with gypsum → Cement powder.
Types of Cement
Common types used in civil engineering:



| Type | Description | Grades (Compressive Strength at 28 days) | Common Uses | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Basic Portland cement; no additives. | 33, 43, 53 MPa | General construction, RCC, prestressed concrete | High early strength, versatile |
| Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) | OPC + Pozzolana (fly ash 15–35%). | Similar to OPC but slower initial | Mass concrete, dams, marine structures | Durable, resistant to chemicals |
| Portland Slag Cement (PSC) | OPC + Blast furnace slag (25–70%). | Similar to OPC | Coastal/marine works, sewage | Excellent sulfate resistance |
| Rapid Hardening Cement | Higher C₃S content; finer grinding. | Higher than OPC | Road repairs, cold weather | Very quick setting |
| Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC) | Low C₃A (<5%). | Similar to OPC | Foundations in sulfate soils | Resists chemical attack |
| Low Heat Cement | Low C₃S and C₃A. | Lower heat evolution | Mass concrete (dams) | Minimizes cracking from heat |
Common grades comparison:
Hydration Process
Cement + Water → Calcium Silicate Hydrate (C-S-H gel) + Calcium Hydroxide + Heat.

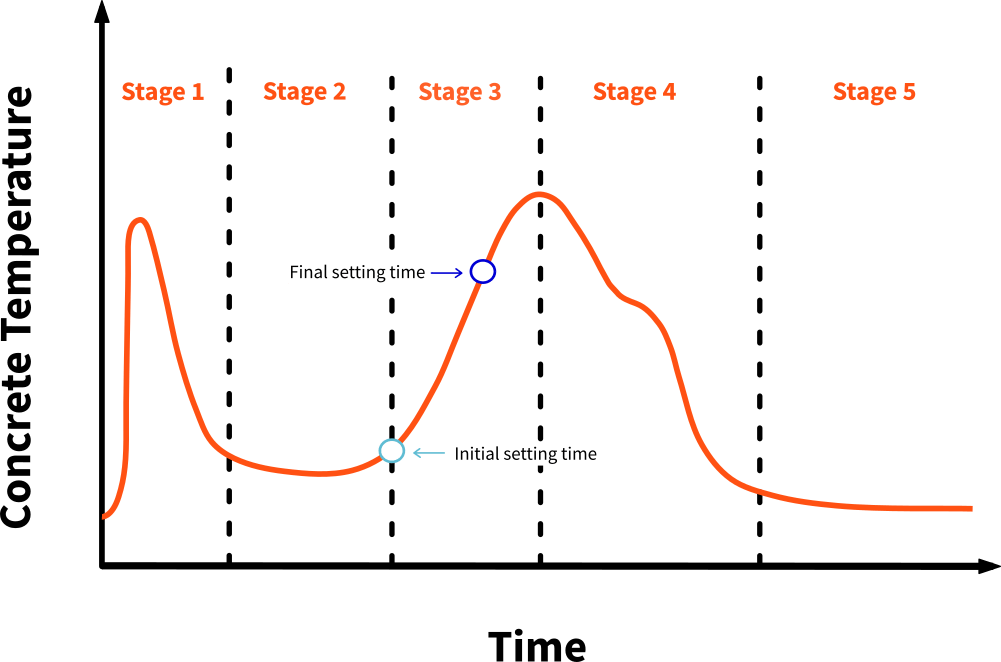
Stages: Initial (minutes), Dormant (hours), Acceleration (strength gain), Deceleration.
Uses in Construction
- Concrete: Cement + Sand + Aggregates + Water (for beams, slabs, columns).


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/difference-between-cement-concrete-and-mortar-2130884-final-ac-5c1aa0e546e0fb0001909553-fd07f31197cd491e85bf0eb8200f6f5e.png)

- Mortar: For plastering, masonry.
- Precast elements, roads, bridges.
Cement provides high compressive strength, durability, and versatility but generates significant CO₂ during production—modern blends like PPC/PSC are more sustainable. Proper curing is essential for optimal strength development.



