Timber in Civil Engineering
Timber (wood) is a natural, renewable, and versatile construction material valued for its high strength-to-weight ratio, aesthetic appeal, thermal insulation, and sustainability. It is widely used in structural framing, roofing, flooring, doors, windows, and formwork. However, it is anisotropic (properties vary with grain direction), susceptible to moisture, insects, and fire, requiring proper selection, seasoning, and treatment.
Classification and Types of Timber
Timber is classified based on origin, durability, and grading.
Common Types (Softwood vs Hardwood):
- Softwoods (from coniferous trees): Fast-growing, lighter, easier to work (e.g., Pine, Fir, Spruce, Deodar). Used for structural framing.
- Hardwoods (from deciduous trees): Denser, stronger, more durable (e.g., Teak, Sal, Oak, Mahogany). Used for flooring, furniture, heavy structures.



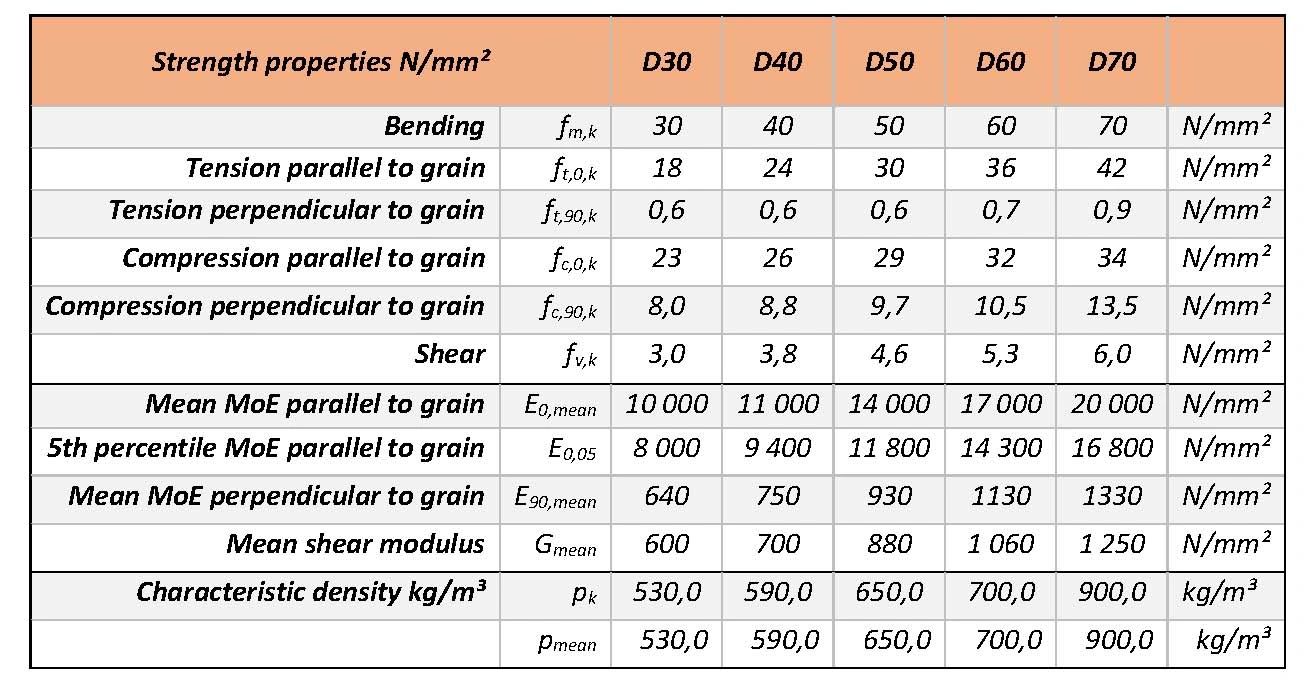
Strength Grading: Visual or machine grading (e.g., EN 338 classes: C16, C24 for softwoods; D30+ for hardwoods). Higher numbers indicate greater strength.
Properties of Good Timber
- Uniform color, straight fibers, dense structure.
- Sweet smell, ringing sound when struck.
- Free from defects, low moisture content (<15% for use).
- High compressive/tensile strength parallel to grain.
- Resistant to decay, insects, and fire (with treatment).
Defects in Timber
Defects reduce strength and durability; classified as natural, seasoning, or conversion-related.
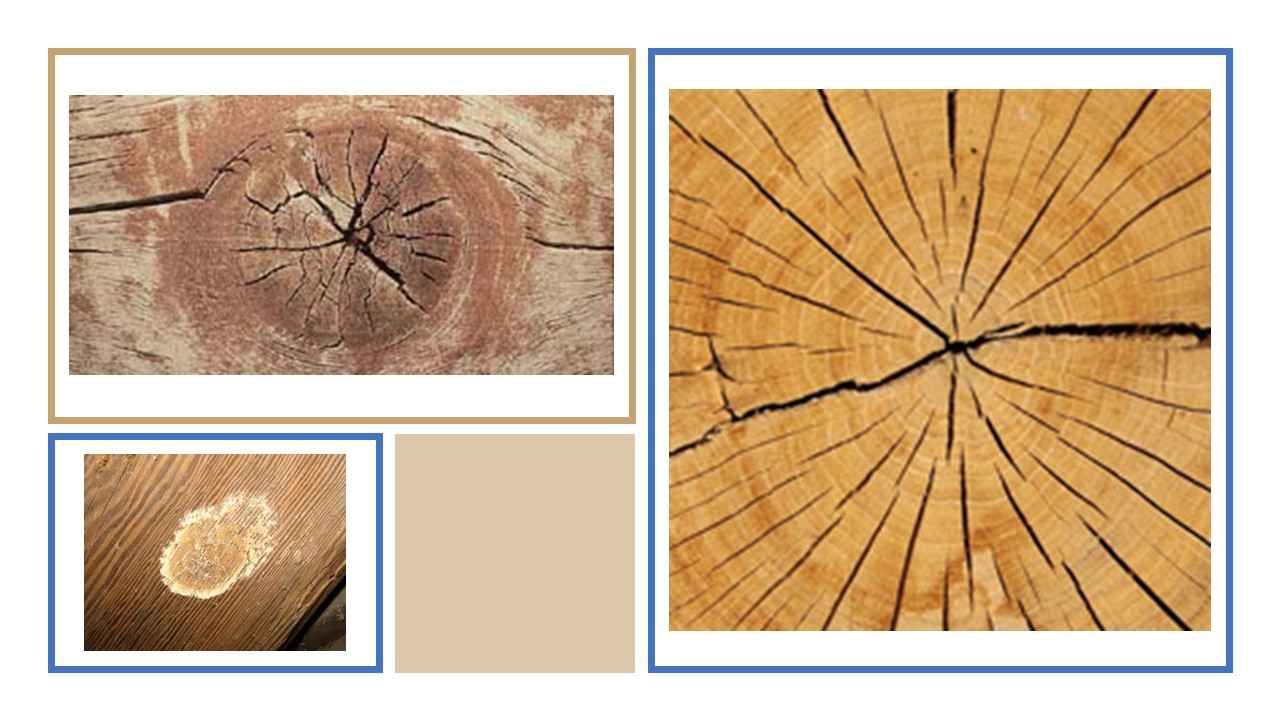



Common defects: Knots, shakes (splits), warping, twists, bow, cupping, insect attacks.
Processing of Timber
- Felling and Conversion: Cutting trees and sawing logs into planks/beams (e.g., ordinary sawing, quarter sawing, tangential sawing).



- Seasoning: Reducing moisture to prevent warping/decay. Methods: Air seasoning (stacking), kiln drying (controlled heat).



- Preservation: Chemical treatments (e.g., creosote, CCA) for durability.
Uses in Civil Engineering
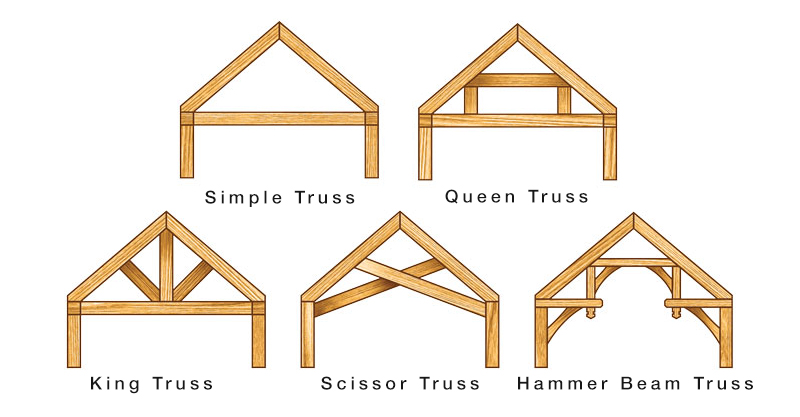
- Structural: Beams, columns, trusses, roofs (king post, queen post trusses).
![Timber Truss Roof Design [A Structural Guide] - Structural Basics](https://structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/3D_truss-1024x683.png)

![Timber Truss Roof Design [A Structural Guide] - Structural Basics](https://structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/char_loads-1024x599.png)
![5 Timber Roof Structures Explained! [2025] - Structural Basics](https://structuralbasics.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Rafter-roof-1024x594.png)
- Non-structural: Doors, windows, partitions, scaffolding.
- Modern: Glulam beams, cross-laminated timber (CLT) for tall buildings.
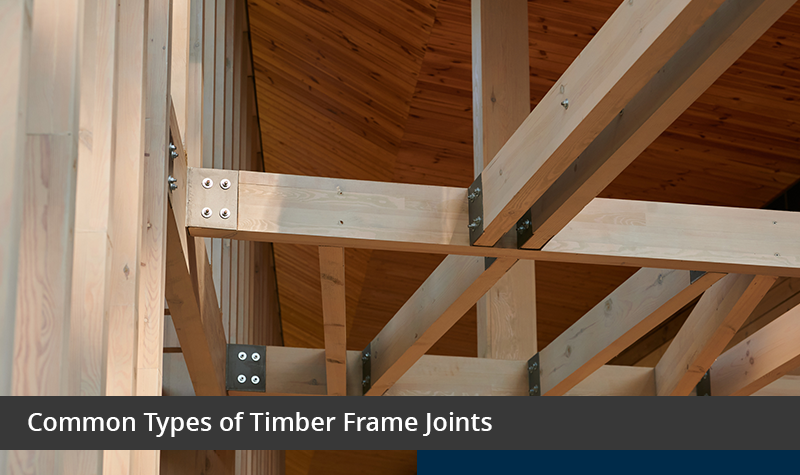
Timber Joints
Essential for connections; traditional carpentry joints provide strength without nails.
Common: Mortise & tenon, lap, dovetail, scarf, bridle.
Timber offers eco-friendly construction but needs protection against environmental factors. Engineered wood products enhance its performance in modern civil engineering.



![13 Types of Wood Joints and Their Uses [with Pictures]](https://i.pinimg.com/736x/db/59/3f/db593f8f70229689b264d4a35d7758cb.jpg)
