Paint in Civil Engineering
Paint is a protective and decorative coating applied to surfaces in buildings and structures. It enhances aesthetics, provides durability, and protects against weathering, corrosion, moisture, and UV damage. In civil engineering, painting is essential for both interior and exterior finishes on walls, ceilings, steel structures, concrete, and wood.
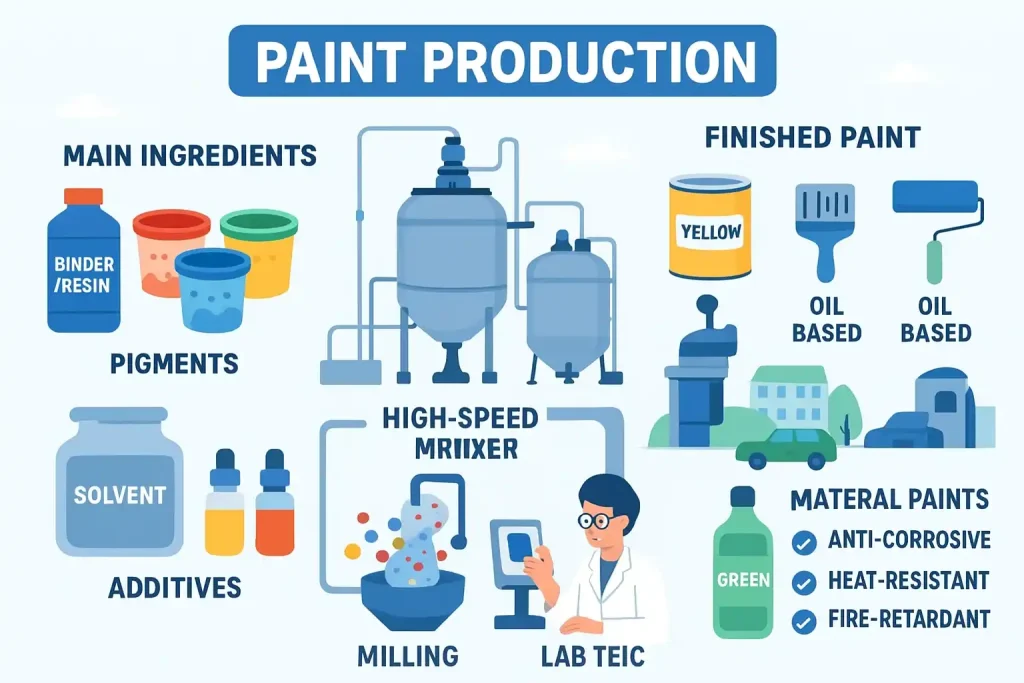
Composition of Paint
Paint typically consists of four main ingredients:
- Pigment: Provides color and opacity (e.g., titanium dioxide for white).
- Binder/Resin: Holds pigment particles together and adheres to surface (e.g., acrylic, oil).
- Solvent/Thinner: Adjusts viscosity for application (water in emulsions, turpentine in oils).
- Additives: Improve properties like drying time, mildew resistance, or flow.
Types of Paint
Common types used in construction:
| Type | Base | Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsion Paint | Water-based (Acrylic/Vinyl) | Quick-drying, low odor, breathable | Interior walls, ceilings |
| Enamel Paint | Oil-based | Glossy, durable, hard finish | Doors, windows, metal surfaces |
| Distemper | Water + Chalk + Glue | Matt finish, economical | Interior walls (budget projects) |
| Cement Paint | Cement-based | Weather-resistant, rough texture | Exterior concrete/masonry |
| Anti-Corrosive Paint | Bituminous/Epoxy | Rust prevention | Steel structures, pipes |
| Texture Paint | Acrylic with fillers | Decorative rough finish | Exterior walls for aesthetics |
| Fire-Retardant Paint | Intumescent | Expands under heat | Fire-prone areas, steel beams |




Surface Preparation
Proper preparation ensures adhesion and longevity:
- Clean surface (remove dust, grease, old paint).
- Repair cracks/holes.
- Sanding for smoothness.
- Apply primer for better bonding.
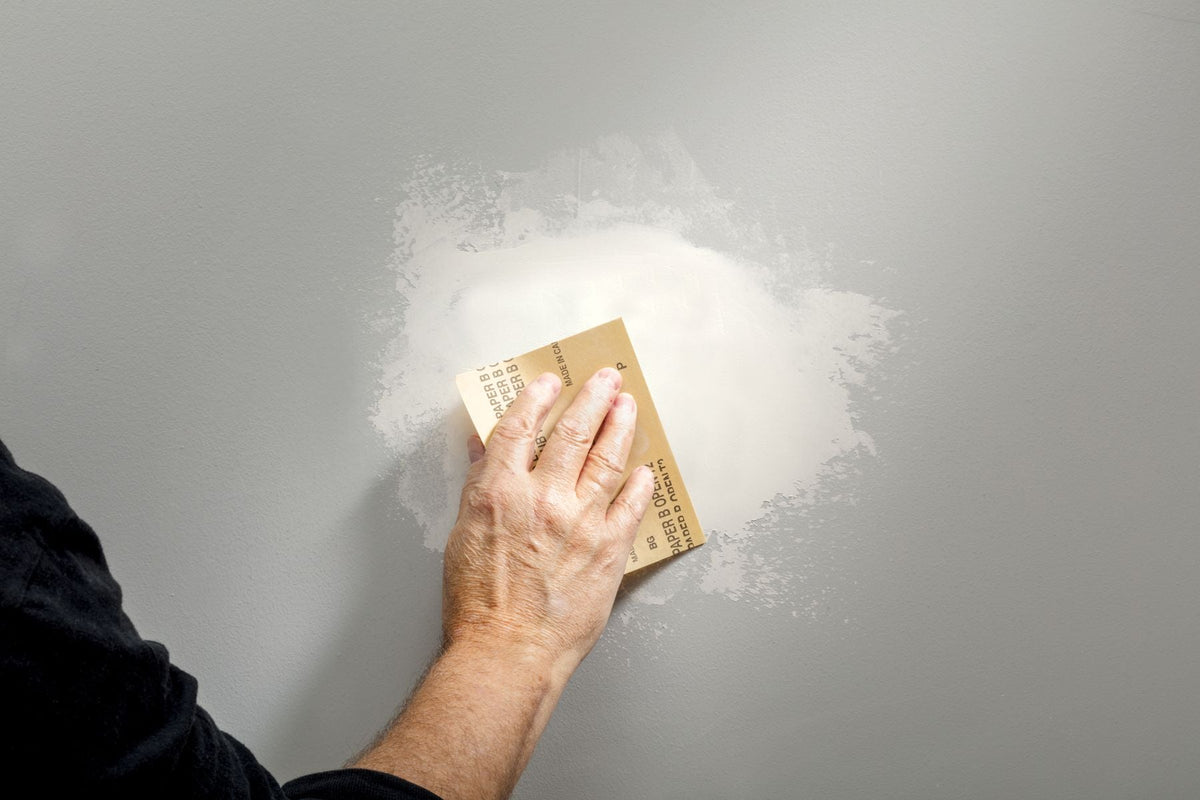
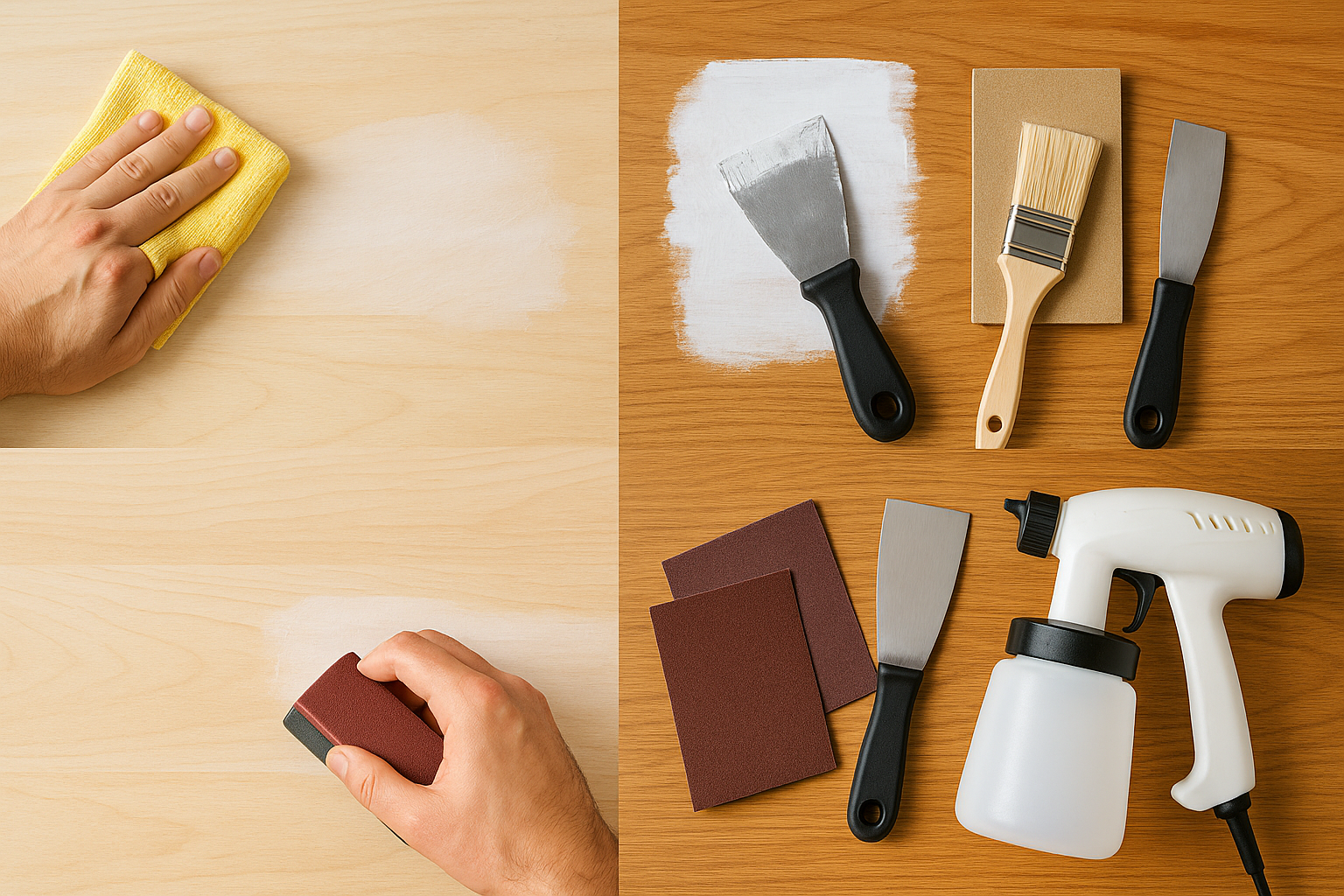



Application Methods
- Brush: For detailed work, edges.
- Roller: Fast coverage on flat surfaces.
- Spray: Uniform finish on large areas.



Typically 2–3 coats: Primer + 1–2 finish coats.
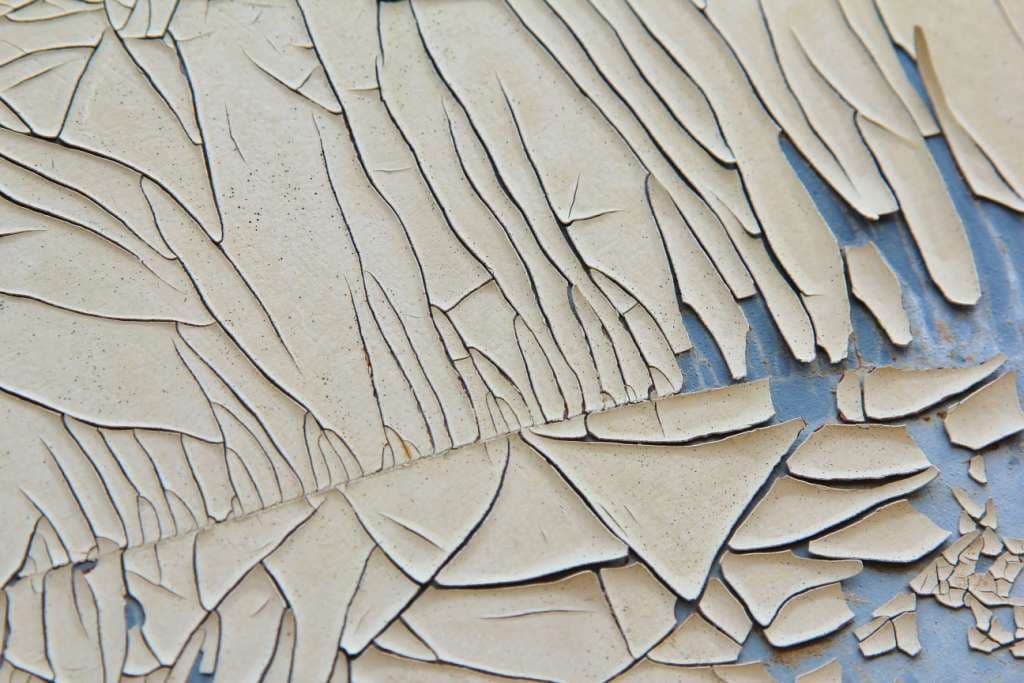
Common Defects and Causes
- Blistering: Moisture trapped under paint.
- Peeling/Flaking: Poor adhesion, damp surface.
- Cracking: Thick coats or movement.
- Fading: UV exposure (use quality exterior paint).




Examples of Painted Surfaces
Interior: Smooth, matt/glossy walls. Exterior: Weather-resistant textured or plain finishes.





Quality paint improves building lifespan, reduces maintenance, and contributes to energy efficiency (e.g., reflective exterior paints). Always follow manufacturer guidelines for best results.